Digestive health is a cornerstone of overall well-being, as it directly impacts nutrient absorption, energy levels, and immune function. The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing essential nutrients, and eliminating waste. Ensuring your digestive health is in optimal condition can help prevent common issues like indigestion, bloating, and more serious conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This article delves into the importance of digestive health, common digestive issues, and effective strategies for maintaining a healthy gut.
What is Digestive Health?
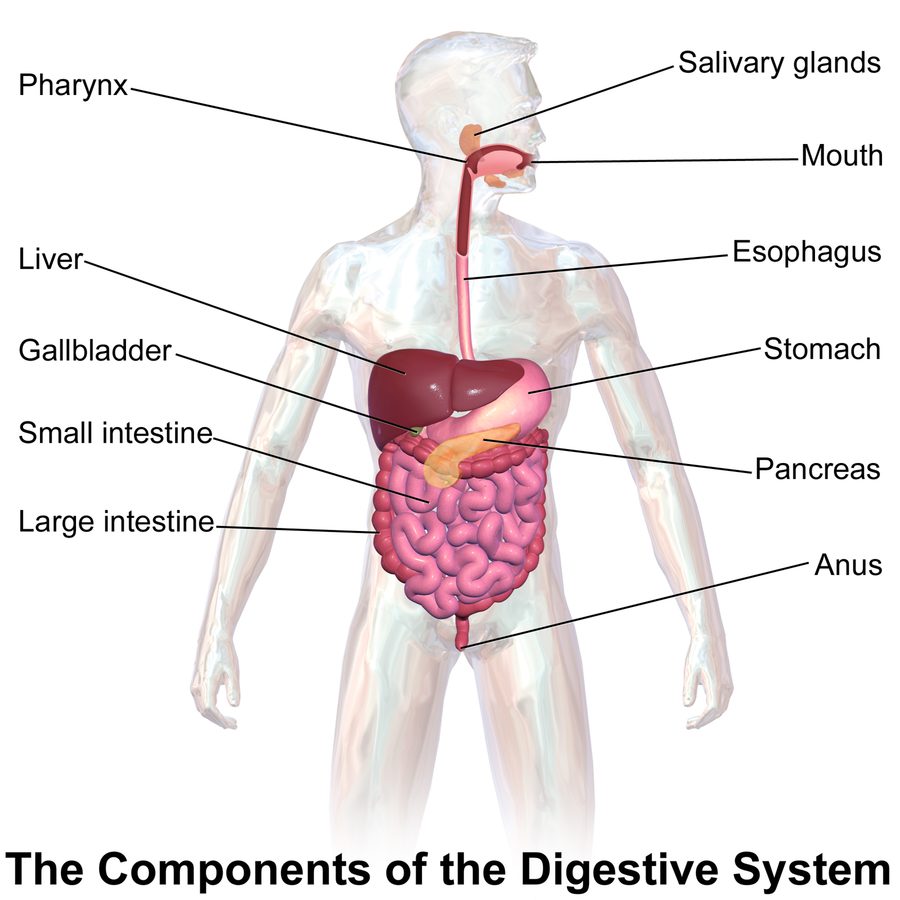
Digestive health refers to the proper functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and other organs involved in digesting food. A healthy digestive system efficiently processes food to provide energy, absorbs nutrients, and removes waste. Good gut health also involves a balanced gut microbiome, the community of beneficial bacteria that play a crucial role in digestion and immune function.
Common Digestive Health Issues
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia): A feeling of discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, often after eating. Symptoms can include bloating, nausea, and heartburn.
- Acid Reflux and GERD: Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn). When this happens frequently, it may develop into GERD, a chronic condition requiring medical attention.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a common disorder characterized by abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, gas, and altered bowel habits. It often involves symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, or a combination of both.
- Constipation: This condition involves infrequent or difficult bowel movements, often resulting in abdominal discomfort. It can be caused by a lack of fiber, dehydration, or inactivity.
- Diarrhea: Loose or watery stools can result from infections, food intolerances, or digestive disorders. Persistent diarrhea may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Key Tips for Maintaining Digestive Health
- Eat a High-Fiber Diet A diet rich in fiber is essential for proper digestion. Fiber helps keep food moving through the digestive tract, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your daily diet.
- Stay Hydrated Drinking enough water is crucial for digestive health. It helps dissolve fats and soluble fiber, making it easier for the body to absorb nutrients and pass waste. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day to support your digestive system.
- Include Probiotics and Prebiotics Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health and improve digestion. Yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha are good sources of probiotics. Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, feed these beneficial bacteria, helping them thrive.
- Avoid Trigger Foods Certain foods can irritate the digestive tract and cause symptoms like heartburn or bloating. These may include spicy foods, fried foods, caffeine, carbonated beverages, and processed sugars. Identify and avoid your personal triggers to maintain gut health.
- Exercise Regularly Physical activity stimulates the muscles of the digestive tract, promoting better bowel movements and reducing the risk of constipation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Practice Mindful Eating Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly can aid in better digestion and nutrient absorption. Avoid distractions while eating, such as watching TV or working, to help your body focus on the digestive process.
- Manage Stress High levels of stress can negatively impact your digestive health, leading to conditions like IBS and ulcers. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can improve digestive function.
The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Digestive Health
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside in the digestive tract. A healthy gut microbiome is diverse, with a balanced ratio of beneficial to harmful bacteria. This balance supports digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system. An imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to digestive problems and even influence mental health due to the gut-brain connection.
- Probiotic supplements can help restore the balance of gut bacteria, especially after taking antibiotics.
- Consuming a variety of plant-based foods can increase the diversity of gut bacteria, which is beneficial for overall health.
Aging and Digestive Health
As people age, the digestive system undergoes changes that can affect digestion, such as a slowed metabolism, decreased enzyme production, and changes in the gut microbiome. Older adults may experience increased symptoms of indigestion, constipation, and other digestive issues. Here’s how to manage these changes:
- Increase fiber intake gradually to avoid bloating and support regular bowel movements.
- Stay active to help maintain healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
- Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on supplements, such as digestive enzymes or fiber supplements, if needed.
Conclusion
Digestive health is an essential component of overall well-being that requires a proactive approach. By incorporating a fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, practicing regular exercise, and managing stress, you can support a healthy digestive system. Additionally, understanding the role of the gut microbiome and the impact of aging on digestion can help you take better care of your digestive health throughout life